Technology research on deburring of precision metal parts
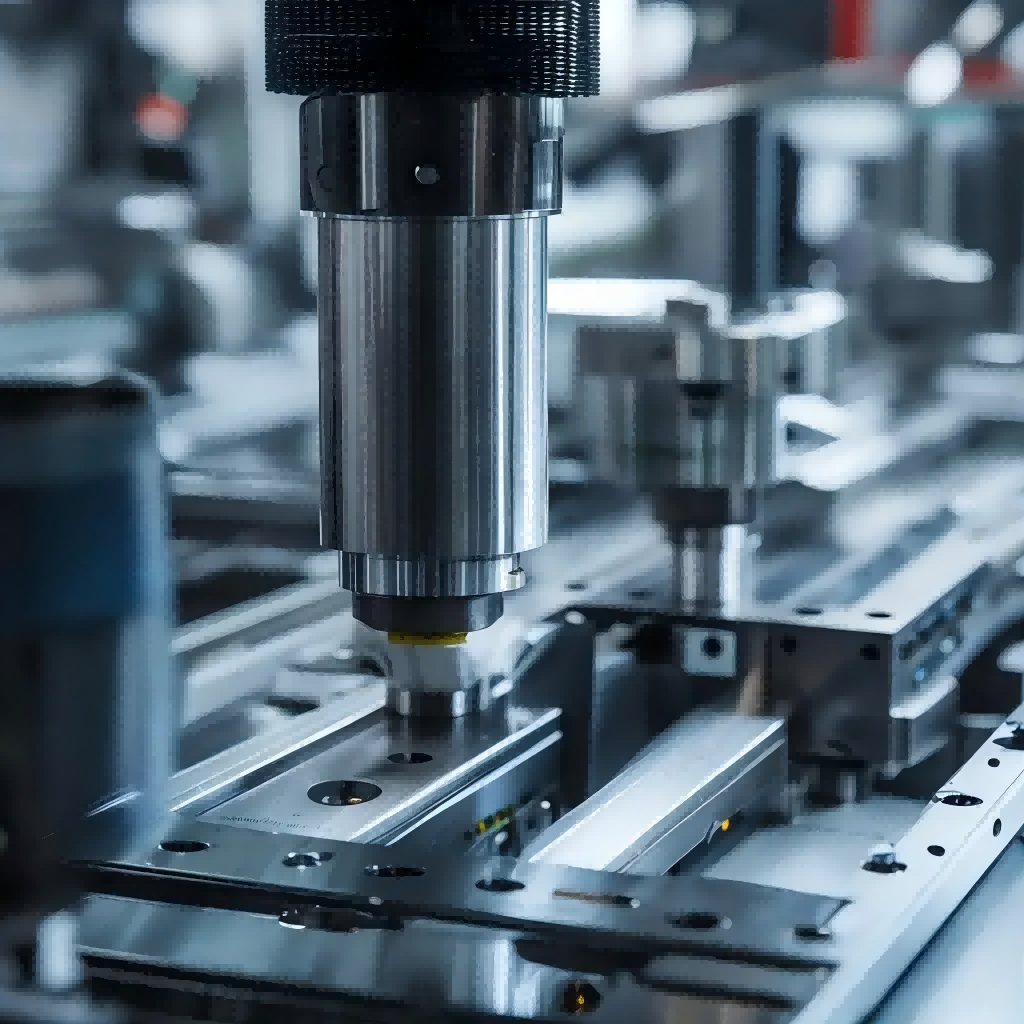
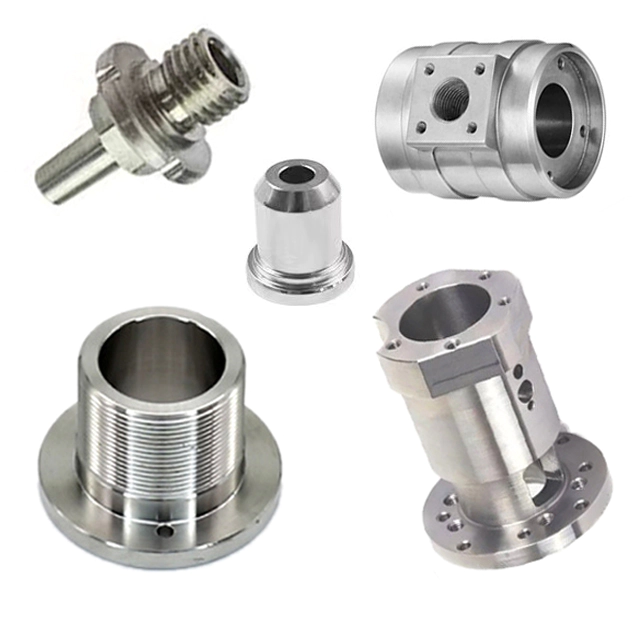
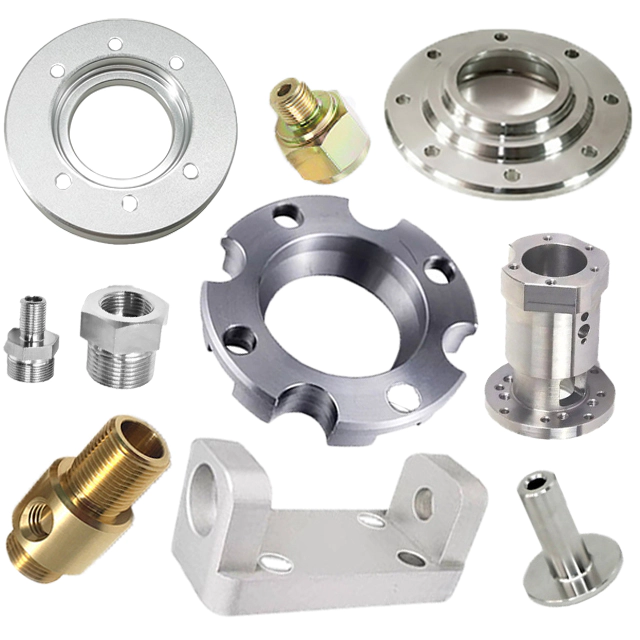
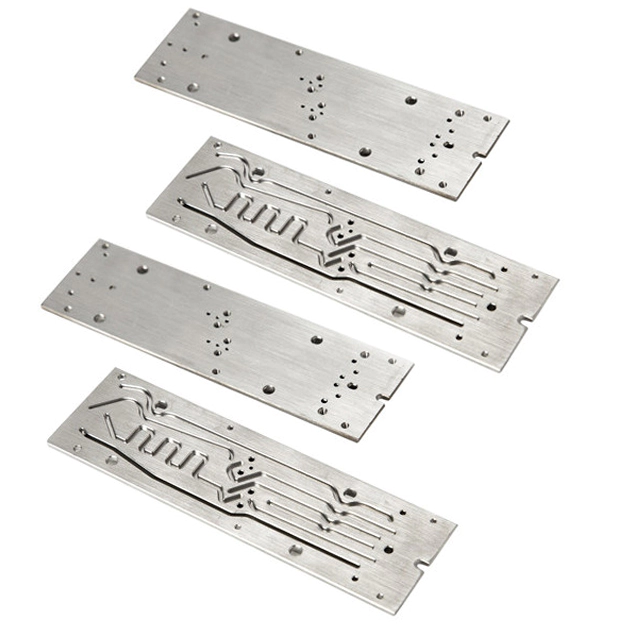
Deburring of precision metal parts is the process of chamfering or rounding sharp corners formed on metal parts during processing. Deburring also removes raised edges and small pieces of material that may remain attached to the workpiece after machining with a cutting tool or grinding wheel. Precision metalworking processes alter the surface of a workpiece to remove machining marks, scaling or pitting. Finishing also enhances the appearance or function of a part and prepares it for subsequent coating processes such as bonding, electroplating or painting. Deburring and finishing are important process steps that should not be overlooked by engineers and technicians designing and manufacturing components.
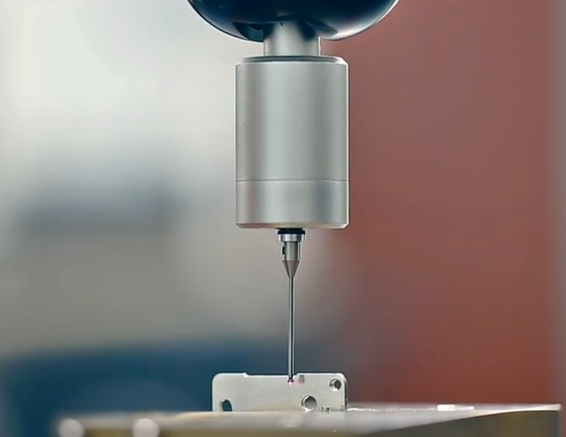
Hand-machined parts are still common in today's modern manufacturing facilities. Many parts machined on complex CNC equipment are still deburred and done using a range of manual, ultrasonic and air tools. Machinists or tool makers utilize files, stones, knives, abrasive sheets/compounds and specialized deburring tools to complete the manufacturing process according to the part geometry and requirements communicated by engineering drawings. Cumbersome and time-consuming manual work increases the cost of the part. Therefore, if many identical parts are produced, automatic deburring and finishing processes are usually specified where possible.
Precision metal machining part quality finishing is a timed batch process that utilizes abrasive media and a rotating or vibrating process vessel to simultaneously deburr and finish multiple machined parts. These machines treat any surface that comes in contact with the medium. Sizes range from small tabletop units for precision metalworking rings and other jewelry to large, twenty-foot rectangular tub units for finishing aluminum aircraft parts. Processing vessels are often fitted with tough rubber liners to protect them from the media and prevent damage to the parts being processed. There are countless media sizes, precision metal machining shapes and material combinations that are selected based on the physical properties of the machined part and how much material needs to be removed to achieve the desired surface finish.
(c)