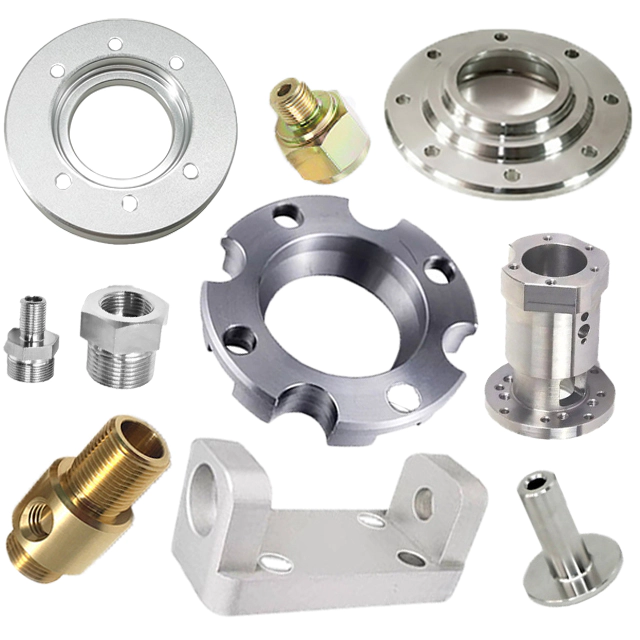
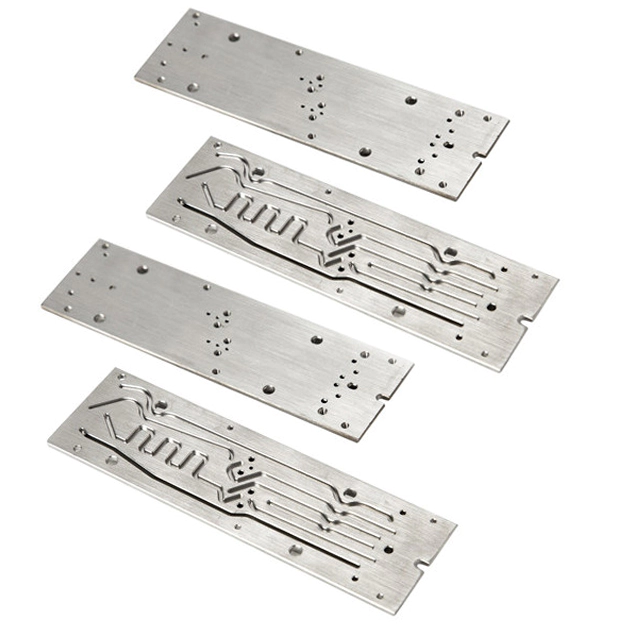
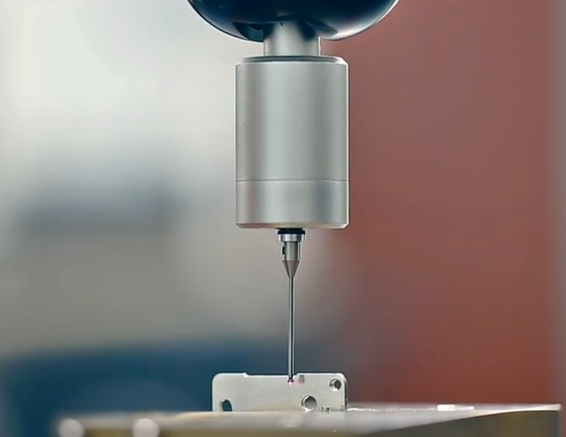
Research on the production of concave ellipsoid precision metal processing parts in the process of customizing non-standard parts
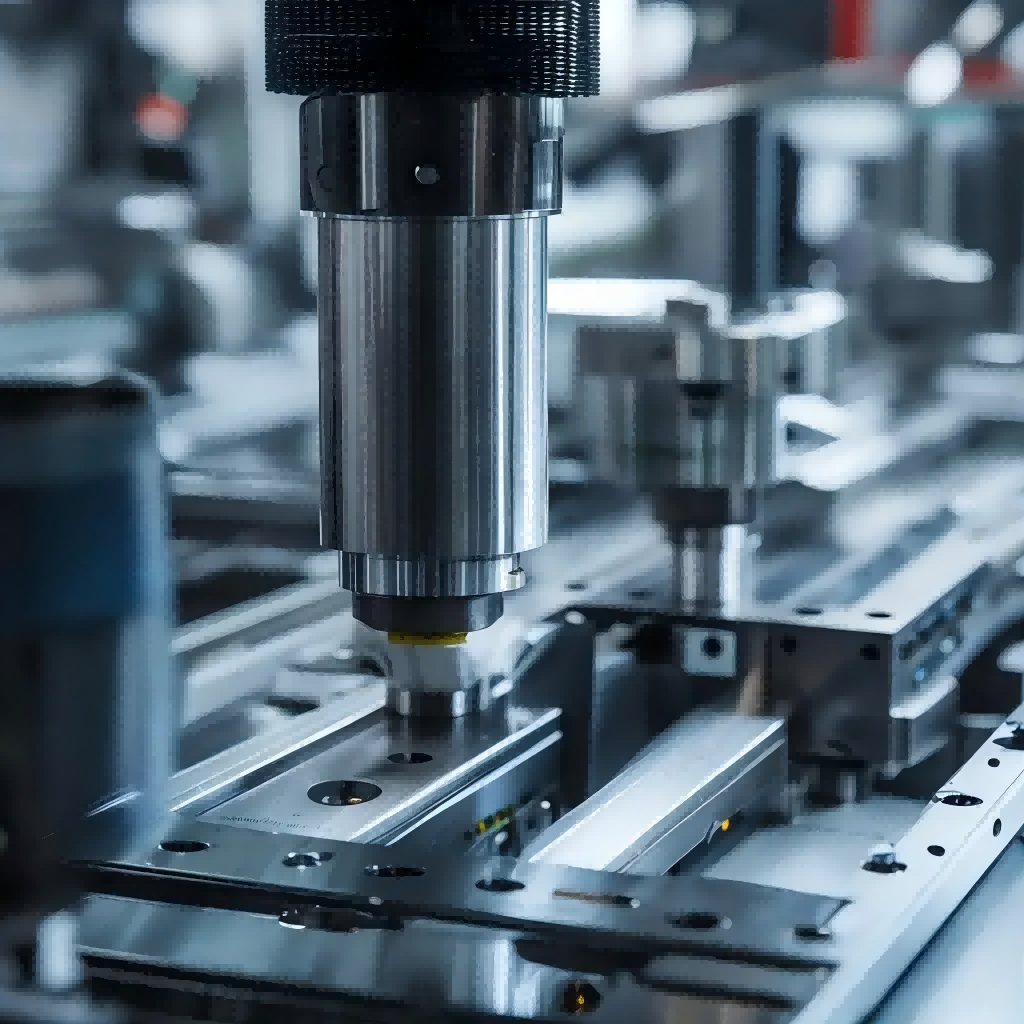
Concave ellipsoid precision hardware is a molded surface. In the process of customizing non-standard parts, we have carried out a series of studies on them. The main program of the CNC lathe directly uses the macro program parameter programming method. On the CNC boring and milling machine, the machining process of the concave ellipsoid is simulated:
First, the surface structure characteristics of concave oval precision hardware processing:
From the CAD part drawing design, the shape of the precision metal processing part is that the concave ellipsoid is elliptical in the projection of each reference plane in the three-dimensional space. The three-dimensional planes each represent the major semi-axis, the minor semi-axis and the high semi-axis of the ellipsoid in the base plane.
The length of each semi-axis of this precision metal processing part can be represented by a parameter variable, and the shape of the ellipsoid can be changed by simply changing the set parameter value. This method is convenient and practical when working with a series of parts with the same path, different sizes and similar shapes.
Second, the analysis of elliptical surface precision metal processing parts:
Due to the use of non-standard customized precision parts, which are not conventional specifications, our engineers have set different parameters for the long axis, short axis and half-axis height of the oval precision metal processing parts. By calculating and selecting the appropriate size ingredients, it avoids wasting raw materials during processing, and at the same time improves processing efficiency.
Fixed clamping with a vise and manual programming of the surface begins with selecting the machining tool according to the characteristics of the surface. Secondly, determine the processing method and process layout of the surface. Then, a mathematical model is built to show the relationship between the relevant parametric variables and programming.
(1) Select the processing tool. When the machining depth is less than or equal to the concave ellipsoid of the high semi-axis, due to its own structural characteristics, the flat-bottomed tool cannot directly process the curved surface at the bottom of the concave ellipsoid, and other types of tools are required to cut off the residual material at the bottom of the curved surface. It is easy to produce height errors (step tool marks) and affect the processing quality, so it should not be directly used as a concave oval finishing tool. Spherical tools can be used to machine the entire concave surface, but are not suitable for removing most of the residual material in the concave body. The tool can be opened first with a keyway cutter, etc., and then the surface finish can be done with a ball nose cutter. Ellipse faces have a minimum radius of curvature, which will limit the tool radius used. If the tool diameter is too large, the tool needs to be cut according to the calculated minimum radius of curvature of the surface.
(2) Determine the surface treatment method. The surface processing of manual programming adopts the two-axis half-height combined with the parametric line difference method, that is, the tool approximates the parametric curve of the inner surface of the layer with a straight line on a certain height layer, then raises or lowers the height layer, and processes the layer according to the layer. . Realize CNC machining of curved surfaces. At the same time, the initial position of the tool in the layer and the cutting and cutting path of the tool can be designed to eliminate tool marks and improve machining quality. However, it is necessary to calculate parametric expressions for the surface profile trajectories in different height layers.
After finishing the processing, we produced this precision hardware part, and measured the actual accuracy. The accuracy is qualified and meets the production standard, and then we plan to quickly complete a series of production.
(c)